Network Cable Types and Specifications
There are three types of network cables; coaxial, twisted-pair, and fiber-optic.
Twisted-pair cables
The twisted-pair cable was primarily developed for computer networks. This cable is also known as Ethernet cable. Almost all modern LAN computer networks use this cable.
This cable consists of color-coded pairs of insulated copper wires. Every two wires are twisted around each other to form pair. Usually, there are four pairs. Each pair has one solid color and one stripped color wire. Solid colors are blue, brown, green and orange. In stripped color, the solid color is mixed with the white color.
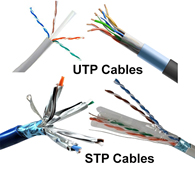
Based on how pairs are stripped in the plastic sheath, there are two types of twisted-pair cable; UTP and STP.
In the UTP (Unshielded twisted-pair) cable, all pairs are wrapped in a single plastic sheath.
In the STP (Shielded twisted-pair) cable, each pair is wrapped with an additional metal shield, then all pairs are wrapped in a single outer plastic sheath.